How to Protect Your Invention – Understanding Patent Types and Applications
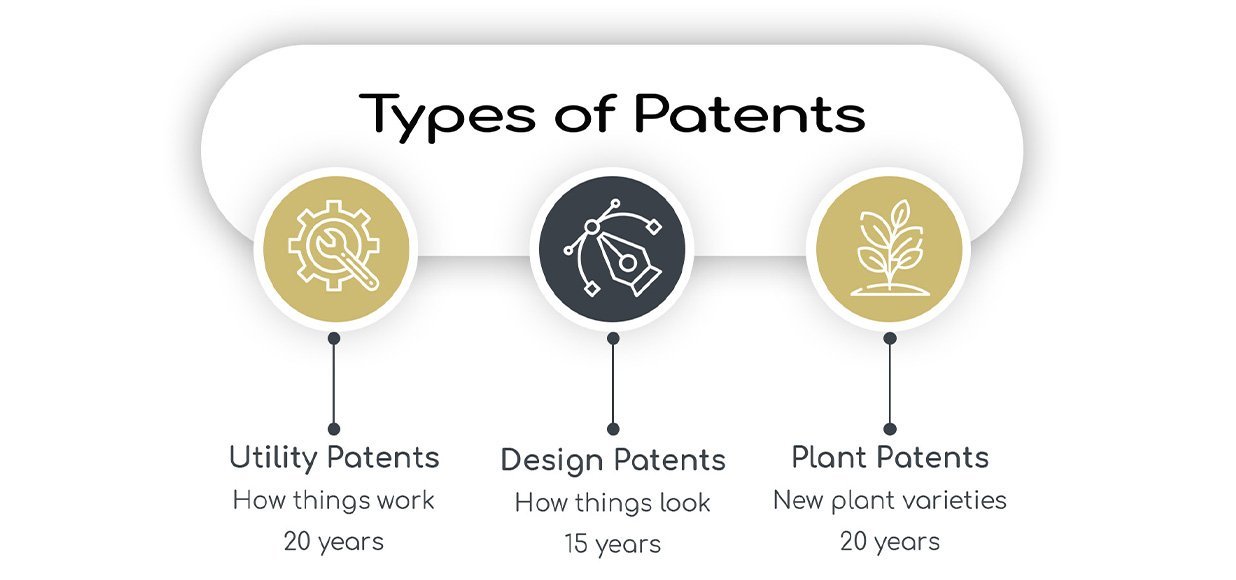
Types of Patents
There are three main types of patents, each serving a specific purpose:
Utility Patent
A utility patent is the most common type. It is granted for new or improved useful processes, machines, compositions of matter, or articles of manufacture.
Design Patent (Industrial Design in Canada)
A design patent (known as an “industrial design” in Canada) protects the ornamental or aesthetic aspects of a product.
Plant Patent
A plant patent is granted for inventing or discovering and asexually reproducing a new variety of plant.
Types of Patent Applications
1. US Provisional Patent Application
A provisional application provides a cost-effective way to establish an early filing date for your invention. It does not require formal claims but must be followed by a non-provisional filing. Licensed Canadian agents can assist with preparing and filing these applications.
2. Non-Provisional (Regular) Patent Application
This is the full, formal submission that describes the invention and defines its scope of protection through claims. It typically includes:
- A detailed description of the invention
- Claims defining the scope
- Technical drawings
- Inventor information and declarations
- Applicable filing fees
3. International Patent Application (PCT)
The Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) provides a framework to seek protection in multiple countries with one initial application.
Life of a Patent
- Utility & Plant Patents – 20 years from the first non-provisional filing date.
- Design Patents / Industrial Designs – 15 years from the grant date (in Canada).
- Maintenance fees must be paid at set intervals to keep a patent in force.15 years from the filing date (in Canada).
Free Consultation
Phone
(416) 871-3466
(647) 818-2532
There are several different ways that you can protect your invention. we provide a free consultation on what the best approaches for you.
